Today, cervical osteochondrosis has become significantly younger. The reason for this is considered to be an increase in living conditions, a significant decrease in mobility during work and rest, and a craze for fast food. They lead to metabolic imbalance and increase trauma to the cervical intervertebral discs, even with minor physical exertion or shocks.

Therefore, it is not surprising that there are many requests on the Internet - osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: symptoms and treatment. We present a brief overview of these questions, as they are always individual in nature and the vertebrologist or neurologist can only answer them in consultation.
Features of the disease
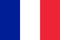
With osteochondrosis of the neck, the discs in the intervertebral space are destroyed. Typically, they perform a shock-absorbing and protective function.
Being between the vertebrae, they prevent the vertebral bodies from touching. When walking and more active movements, they can compress, giving flexibility to the spine. In addition, due to the disc-ligamentous apparatus, passages are created for the nerves leaving the spinal cord.
When the discs and ligaments are destroyed, the vertebrae begin to rub against each other. Friction causes pain and other discomfort in the neck. As the vertebrae move closer together, the nerves become compressed and additional symptoms appear in the parts of the body for which the affected neurons are responsible. Neurological symptoms occur.
Osteochondrosis can affect any part of the spine and symptoms vary. Disc destruction can occur in several areas at the same time.
A greater amount of load falls on the lumbar spine, which means that the discs and ligaments here are more often subject to changes. But it is osteochondrosis of the cervical region that causes the most suffering in humans. After all, the main vessels supplying blood to the brain pass through the neck, and there are many nerves and nerve endings.
Statistics show that the cervical region is the most affected. Of all the parts of the spine, it is the most mobile. In a video on the internet you can see how the disease develops and its complications.

The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women are not fundamentally different from the symptoms that occur in men. There is a difference: the most common symptom of the disease in women is headache.
Causes
The classic causes of the development of cervical osteochondrosis include:
- low mobility, lack of adequate physical activity;
- disturbances in metabolic processes;
- salt deposits, mainly in the cervical region;
- unbalanced diet;
- incorrect body position when working at a computer, driving a car or during other static activities.
If you are predisposed to deforming joint diseases or salt deposits, the risk of developing a disease due to an unhealthy lifestyle increases.
Classification of clinical manifestations
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, symptoms and treatment of pathology are closely interconnected, but complex therapy is prescribed only after instrumental clarification of the diagnosis. Currently, there is the following classification of manifestations.
Radicular syndromes or cervical radiculitis
Radicular syndromes are the medical term for a group of symptoms that occur due to compression of nerve roots located between the vertebrae in the neck. Initially, this compression manifests itself in the form of paresthesia - numbness, tingling and a sensation of "goosebumps" on the skin.
Ignoring and not treating such manifestations leads to further progression of the disease. Acute pain occurs (rapid or delayed), which evolves into chronic pain syndrome.
The characteristic manifestations of cervical radiculitis depend on the location of the degenerative processes, that is, between which vertebrae the nerve roots were compressed:
irritant reflex syndrome
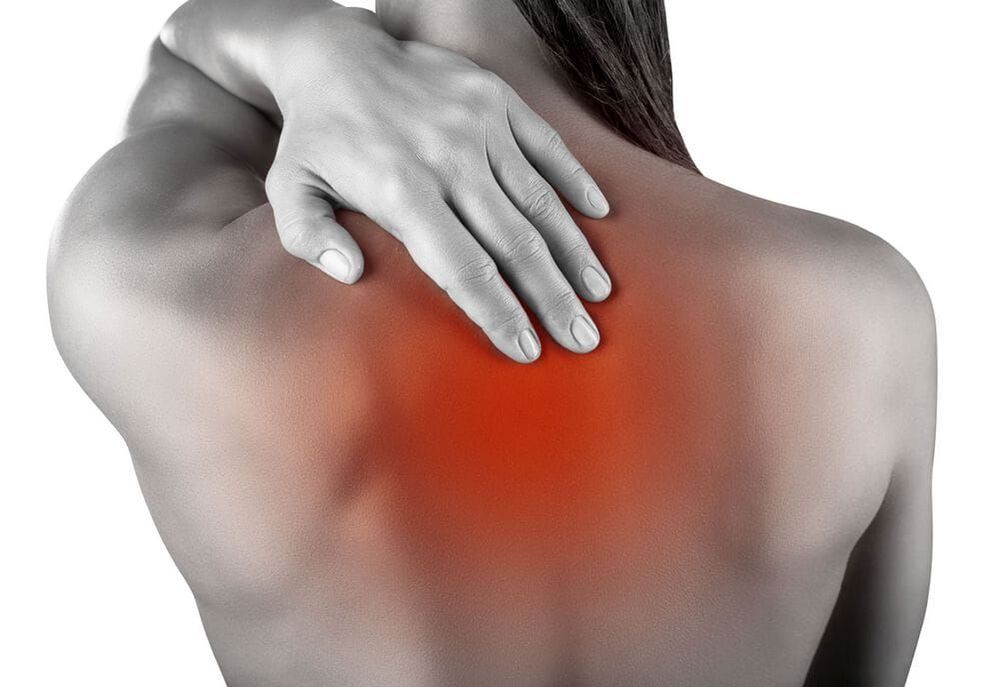
Pain in irritant reflex syndrome when the roots of the lower cervical vertebrae are pinched occurs between the shoulder blades.
This syndrome is characterized by diffuse, sharp pain in the neck, neck or upper back. They occur after sleep or during the beginning of movement after long static maintenance of a position. It is possible for the pain to painfully radiate to the heart or shoulder joint.
Vertebral artery syndrome

Osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine, symptoms (and its treatment) can manifest as combined signs in Vertebral Artery Syndrome:
- headaches – punctual, pulsating or burning, spreading diffusely;
- locations - above the eyebrows, on the temples, on the top of the head, on the back of the head;
- pain is constant, but sometimes occurs in the form of attacks;
- the intensity of pain increases after the first movements in static positions;
- in weakened people, nausea may occur, coordination of movements may be impaired, dizziness and fainting may occur;
- Possible decrease in hearing and visual acuity, "bunnies" in the eyes, tinnitus, snoring.
On a note! Often, the only signs of cervical osteochondrosis are pharyngeal symptoms. These include: pain, dryness and/or difficulty swallowing. However, the cost of ignoring such symptoms can be enormous. These symptoms are inherent to some inflammatory diseases that can develop into cancer.
cardiac syndrome
Preliminary diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is often complicated by the presence of cardiac syndrome in the patient.
Is characterized by:
- increased heart rate;
- attacks or prolonged pain in the heart region, which are often confused with angina pectoris;
- Chest pain worsens after sudden movements or heavy lifting.
Therefore, if angina is detected, an experienced doctor will direct the patient to undergo an x-ray of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae, since with a parallel diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, the symptoms and treatment at home will be specific.
For example, a vertebrologist is obliged to warn the patient that if "heart pain" is not relieved with nitroglycerin or other coronary dilating drugs, they should not be taken several times in a row in a short period of time. Just drink ibuprofen or Nurofen forte.
For your information! There is another way to distinguish a true angina attack from a painful coronary syndrome. With the latter, the patient is able to walk quickly.
Minor symptoms
Nausea
Feelings of nausea and belching are the result of blood circulation problems in the brain. Often, patients associate this symptom with nutritional errors, begin to limit the amount of food they eat and make changes to their diet.
Nausea and belching can reduce your appetite. All these phenomena lead to the fact that a person begins to lose body weight and the balance of nutrients in the body is disturbed.
An attack of nausea can end in vomiting, which also occurs with careless turning of the head, bending the body or strong physical activity. In this case, poor circulation leads to insufficient nutrition of the inner ear and balance center.
Feeling of suffocation
A feeling of shortness of breath occurs when the phrenic nerve is compressed in the cervical region of the spine. This important nerve is an element of the cervical plexus and regulates the depth of breathing and the frequency with which respiratory movements are performed.
Patients complain of difficulty breathing with all their might. Shallow breathing leads to a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood, shortness of breath occurs, and in severe cases, suffocation occurs.
At night, breathing may stop, often occurring together with a snoring attack. Nighttime problems are caused if the person is lying in an uncomfortable position and the head and neck are not in the anatomically correct position.
If these problems are accompanied by unsatisfactory hygiene of the room where the person sleeps, when the room is poorly ventilated, dusty and there is no flow of clean air at night, the patient has hypoxia. The lack of oxygen occurs in all tissues of the body, when waking up the patient will not feel rested
Buzzing sensation
Tinnitus occurs due to problems with the blood supply to the vestibular apparatus. Blood vessels pass through the cervical vertebrae of the spine.
Disorders in the parts of the inner ear cause sensations of various sounds:
- background hissing noise;
- ringing, squeaking.
A complex of these complaints is usually called cochlear or cochlear syndrome.
Important: if the patient does not consult a doctor with these symptoms, over time there will be a decrease in hearing acuity.
Patients often think that such disorders are associated with the auditory analyzer itself. Even a doctor may have difficulty understanding the situation, especially if there are no clear signs of osteochondrosis.
However, when there are problems with the vertebrae, specific auditory symptoms appear. Osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra can be differentiated by the features of its occurrence, therefore, sounds appear when a person remains in the same position for a long time.
Throat problems
Often, osteochondrosis can only manifest itself through a complex of pharyngeal symptoms:
- Sore throatoccurs without connection to food intake, it is possible to draw the difference between the appearance of symptoms and sudden movements of the head and neck.
- Foreign body sensation in the throatappears and disappears.
- There are complaints of itching and dry throat, strong unpleasant sensations can make the patient want to cough. The cough will cause an increasingly dry and scratchy sensation. These complaints are a consequence of simultaneous damage to nerve fibers and blood vessels.
Important: such symptoms can be observed with inflammation in the region of the cervical vertebrae and with the occurrence of tumors.
Vision problems

Deterioration of visual function is less common; they occur more often in people with atherosclerotic lesions of the head vessels and with a decrease in general pressure.
The vessels that supply the eyes also pass through the cervical vertebrae; with its osteochondrosis, the following complaints arise:
- the appearance of a "veil" over the eyes;
- decreased clarity and visual acuity;
- the appearance of black dots or rods;
- Difficulty focusing on a specific subject.
Symptoms are not constant. Patients notice that vision sometimes worsens and sometimes improves.
A distinctive symptom of osteochondrosis is the inability to influence the state of vision with the help of glasses, medications and gymnastics. Eliminating symptoms is only possible after treating the root cause of the problem.
Loss of consciousness
Impaired blood supply to the brain can lead to loss of consciousness or syncope. This happens when blood flow to the brain is temporarily interrupted.
In this case, the pinching does not necessarily occur in the cervical region, just irritation due to the deformed structures of the vertebrae is sufficient. In response to this effect, a significant spasm occurs in the arteries.
Consciousness returns to a person quickly. This is facilitated by changing the position of the body. A person who has lost consciousness must be placed in a horizontal position with their legs raised. This way, blood from the lower body will help restore blood supply to the suffering brain.
As a rule, these short-term conditions do not bring any complications or consequences. If the interruption of blood flow to the brain is stronger, consequences are possible.
Important: after loss of consciousness, the patient must consult a doctor for an examination and to prevent recurrent attacks.

Despite the short duration of the condition, a person who has lost consciousness needs to call an ambulance.
Blood pressure problems
The presence of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine causes spikes in blood pressure. For people past middle age and the elderly, this can be especially noticeable. This is due to the fact that the center responsible for the vascular response to changes in the external environment is located in the brain and also suffers from insufficient blood supply.
The presence of irritating factors in the form of a deformed vertebra aggravates the situation. This is how the symptoms of VSD arise against the background of cervical osteochondrosis. Depending on the person's predisposition, hypertensive or hypotonic crises occur. One type of crisis often gives way to another.

Temperature fluctuations
Temperature fluctuations are not a specific symptom of osteochondrosis. If the body temperature rises, it means that a focus of infection or neoplasia has appeared in the body. The immune system responds in the form of temperature.
However, patients may feel heating and even burning of the skin at the location of the problem, that is, the back of the neck.
When several symptoms combine, the person begins to feel unwell. General health worsens, mood drops, irritability and inattention appear. For a patient with severe pain or blurred vision, it becomes difficult to carry out everyday tasks and perform productive work activities.
Important: if any complaints, even not related to back problems, prevent you from leading a normal and normal lifestyle, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible and determine the cause of the problem.
Danger of disease
Cervical osteochondrosis represents a great danger, since the area affected by it are the most important vascular pathways that supply the brain and spinal cord with numerous nerve branches. All symptoms of osteochondrosis have a significant negative impact on the patient's well-being and quality of life.
But this disease has life-threatening complications:
- Intervertebral hernia is considered the next stage in the development of osteochondrosis. It occurs in the absence of treatment. People who suffer from neck or back pain for a long time without seeing a doctor receive exactly this diagnosis.
- Compression of the spinal cord processes causes damage to them and radiculopathy develops. Along with this, growths and osteophytes form on the vertebrae. All this threatens the patient with loss of mobility and sensitivity of the areas for which the affected nerve fibers are responsible.
- One of the most dangerous complications is vertebral artery syndrome with cervical osteochondrosis. This artery supplies important parts of the brain - the medulla oblongata and the cerebellum. When this vessel is compressed by osteochondrosis, ischemia of the spinal cord and brain occurs. There is a risk that the disease will end in a stroke.
- If the disease has not been treated for years, in the presence of vertebral deformities, there is the possibility of injury to the spinal cord itself, located inside the spinal column. The cost of lack of treatment is organic injuries incompatible with life.
If a person discovers symptoms of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, they should consult a specialist as soon as possible. Deformation of the vertebrae can cause severe trauma to the spinal cord and this is very dangerous for humans.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
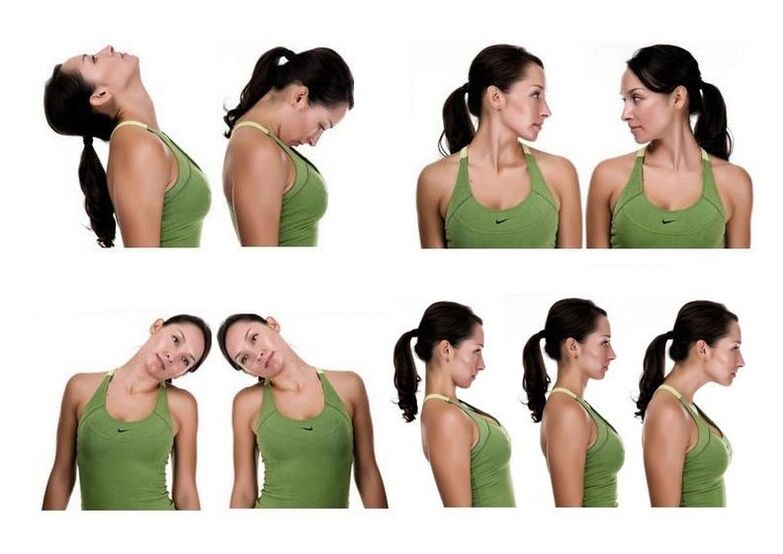

Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis and treatment at home require the approval of the treating specialists. The video in this article with a set of exercises for the neck muscles has not been posted. There are many of them on YouTube.
However, you should know that the instructions for exercise therapy with this diagnosis prohibit:
- run;
- perform any jumping movements;
- stimulate the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck with dynamic exercises, especially with weights or resistance.
Important! If cervical osteochondrosis worsens, symptoms and treatment with physical exercise, self-massage and physiotherapeutic procedures are suspended. In the acute period, visits to the chiropractor are also prohibited. Rest and drug therapy with analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets and ointments are indicated.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with folk remedies is not very effective and is possible as an auxiliary method of therapy at the rehabilitation stage. However, vertebrologists praise leech treatment and categorically do not recommend that bee sting treatment also helps in therapy;
Allergy is an insidious disease, the occurrence of which is impossible to predict, and an acute allergic reaction - Quincke's edema can lead to anaphylactic shock and be fatal.
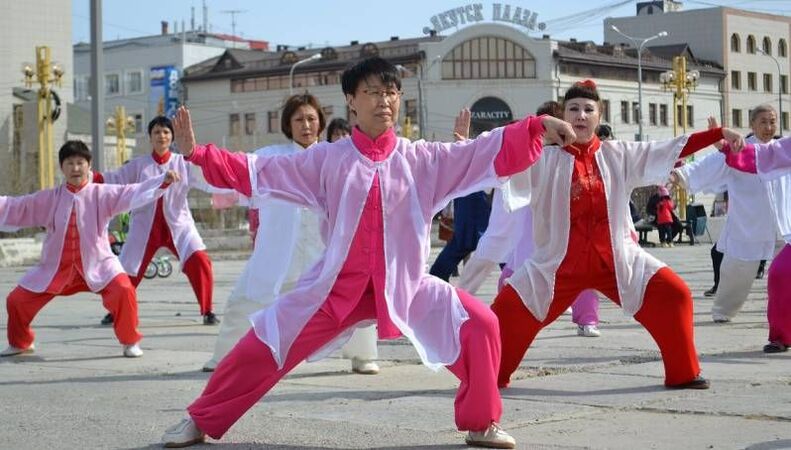

Among the non-traditional methods of treating cervical osteochondrosis, we can recommend:
- dynamic and static yoga classes;
- Wushu, Taiji and Qigong gymnastics;
- acupuncture and Su-Jok.
In addition to daily physical exercise, it is necessary to give up bad habits, monitor your daily diet and balance your diet, as well as do special morning exercises for osteochondrosis of the lower back. The weekly menu should include raw and half-cooked vegetables, fresh seasonal fruits, fermented milk drinks and daily dishes.
Natural meats of dietary varieties and fish from the herring or salmon family should be consumed every other day. Replace coffee and tea with rosehip decoction and natural juices.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is a long process that will take not months, but years. Osteochondrosis cannot be cured, but significant remission can be achieved. The results will depend solely on the patient himself, on his commitment to following the recommendations and maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle.
Common questions
What are the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can manifest as pain in the neck, shoulders, arms, dizziness, tinnitus, numbness or tingling in the arms and limited neck mobility.
How can you treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at home?
To alleviate the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you can use relaxation methods, exercises to strengthen the neck muscles, massages, hot compresses and the use of analgesic ointments and gels.
What exercises help with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
To strengthen the neck muscles and alleviate the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, exercises for stretching and strengthening the neck muscles, rotating the head, flexing and turning the neck, as well as exercises to improve posture are useful.
Useful Tips
Tip #1
With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, it is recommended to perform special exercises to strengthen the muscles of the neck and back. This will help improve blood circulation and reduce stress on the spine.
Tip #2
You can use cold compresses or warm wraps to ease pain and reduce inflammation. Cold helps reduce swelling, while heat improves blood circulation and relaxes muscles.
Tip #3
It is important to monitor your posture and avoid staying in the incorrect position for long periods of time. Taking regular breaks to stretch and adjust your working position can reduce stress on the cervical spine.